Disruptions in the Urea Cycle and Cancer
How hypoxia reprograms nitrogen metabolism in cancer cells
Summary
- Hypoxic Reprogramming: HIF-driven mechanisms fundamentally alter urea cycle function
- Metabolic Rewiring: UC suppression affects cancer cell growth and survival
- Biosynthetic Advantage: Frees up precursors for growth pathways
- Ammonia Tolerance: Cancer cells utilize ammonia for growth

Hypoxia and Urea Cycle Reprogramming
Hypoxia fundamentally reprograms the urea cycle (UC) via HIF-driven transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. This rewiring affects growth and survival. UC suppression frees up biosynthetic precursors at the expense of ammonia clearance, allowing moderate sub-toxic ammonia to fuel growth pathways.
HIF-Mediated Control
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) serves as a master regulator of cellular responses to low oxygen conditions. Through both transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms, HIF orchestrates the reprogramming of urea cycle enzymes, shifting cellular priorities from waste removal to growth support.
The Urea Cycle
The urea cycle comprises five enzymes that convert ammonia and carbon dioxide into urea, facilitating nitrogen waste removal from the body. This essential metabolic pathway prevents the toxic accumulation of ammonia while maintaining nitrogen homeostasis.
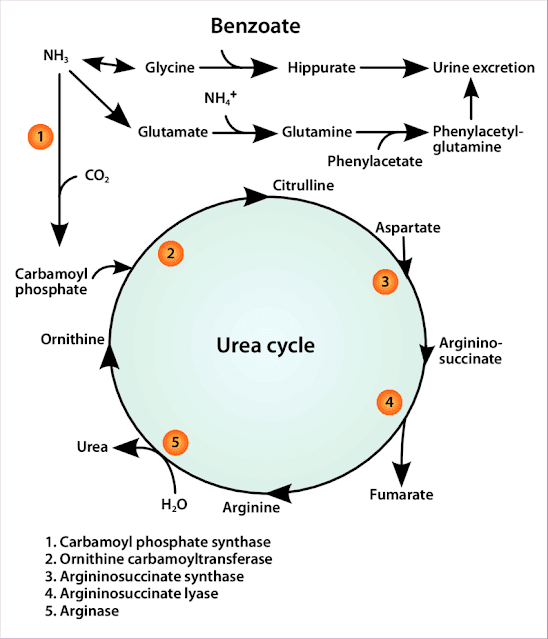
Key Regulatory Elements
Rate-Limiting Enzyme
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (CPS) is the rate-limiting enzyme in the urea cycle, partially regulated by HIF-1, a transcription factor often implicated in cancer development. This regulatory relationship makes CPS a critical control point in cancer metabolism.
Metabolic Interconnections
The urea cycle is interconnected with the citric acid cycle, a central hub of cellular metabolism. This connection allows for coordinated regulation of energy production and nitrogen disposal.
Hormonal Regulation
Hormones like insulin and glucagon influence urea cycle enzyme activity, integrating nitrogen metabolism with overall metabolic status and nutrient availability.
Cancer Implications
Metabolic Advantage in Cancer
By suppressing the urea cycle, cancer cells redirect metabolic resources away from ammonia detoxification and toward biosynthetic pathways that support rapid growth and proliferation. This metabolic flexibility represents an adaptation that enhances cancer cell survival under stress conditions.
Growth Pathway Fueling
The tolerance of moderate sub-toxic ammonia levels allows cancer cells to utilize nitrogen-containing compounds more efficiently for biosynthesis. This represents a trade-off between detoxification capacity and growth potential, favoring rapid proliferation over waste management.
| Normal Cell | Cancer Cell (ASS1-Silenced) | |
|---|---|---|
| Urea Cycle Status | Active. Detoxifies Ammonia. | Broken. Accumulates Ammonia. |
| Ammonia Level | None/Low. | High (Accumulates in TME). |
| Effect on T-Cells | T-cells function normally. | T-cells are stunned/exhausted (Immune Evasion). |
| Metabolic Fate | Excreted as Urea. | Recycled via GDH to make Glutamate (Fuel). |
| Normal Cell | Cancer Cell (ASS1-Positive / Overexpressed) | |
|---|---|---|
| Urea Cycle Status | Active. Detoxifies Ammonia. | Hijacked / Synthetic. Uses the cycle enzymes (ASS1/ASL) to synthesize massive amounts of Arginine from Citrulline. |
| Key Accumulation | None (Waste is excreted). | Polyamines. The Arginine produced is immediately converted into Putrescine, Spermidine, and Spermine. |
| Effect on T-Cells | T-cells function normally. | Resource Competition. The tumor consumes Citrulline/Arginine so rapidly for growth that it can outcompete T-cells. Critically, it is Resistant to Arginine Deprivation Therapy. |
| Metabolic Fate | Excreted as Urea (Waste). | Diverted via ODC (Ornithine Decarboxylase) to make DNA/Biomass (Rapid Proliferation). |
A eUREkA! moment: The *T-Cell* Urea Cycle
Citrulline & Bicarbonate: Metabolic Reprogramming for Cancer Immunotherapy.
Related Metabolic Information
Cellular Respiration: Understanding the interconnected citric acid cycle
Hypoxic Metabolism: HIF-mediated reprogramming affects multiple metabolic pathways beyond the urea cycle
Key Concepts & Further Reading
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF): Master regulator of cellular responses to low oxygen conditions, controlling multiple metabolic pathways including the urea cycle.
Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase: Rate-limiting enzyme of the urea cycle, representing a critical control point for nitrogen metabolism in cancer cells.
Metabolic Flexibility: The ability of cancer cells to reprogram metabolic pathways to support growth and survival under various stress conditions.
Last updated: September 2025


%20(3).png)

No comments:
Post a Comment