Triple-negative breast cancer: Synergistic combinations of natural compounds and drug repurposing
Solely intended for informational use, none of my writing constitutes medical advice.
Strategy - an integrative approach to cancer management: example of a multi-layered approach using coactive combinations of natural substances and drug repositioning.
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC): An aggressive subtype of breast cancer characterized by the absence of estrogen receptors (ER), progesterone receptors (PR), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) expression. This makes it resistant to many targeted therapies, leading to a poorer prognosis compared to other breast cancer subtypes.
Synergistic Therapies
 |
| click to enlarge the diagram |
Mechanisms and Pathways
.jpeg) |
| click to enlarge the diagram |
To save and/or print the diagrams, click on the diagram, right-click and select open image in a new window and select save image as. Ctrl + P on a PC or Command + P on an Apple computer to open the print options, right-click again for print options, or click to zoom in. Ctrl+F ⌨ to search this page.
Supporting research and studies
Metabolic recycling of ammonia via glutamate dehydrogenase supports breast cancer biomass. Spinelli JB, Yoon H, Ringel AE, Jeanfavre S, Clish CB, Haigis MCScience. 2017 Nov 17;358(6365):941-946. doi: 10.1126/science.aam9305. Epub 2017 Oct 12. PMID: 29025995; PMCID: PMC5748897. 🛈
Metformin-induced ROS upregulation as amplified by apigenin causes profound anticancer activity while sparing normal cells. Warkad, M.S., Kim, CH., Kang, BG. et al. Sci Rep 11, 14002 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-93270-0
Mitochondrial complex I activity and NAD+/NADH balance regulate breast cancer progression
Antonio F. Santidrian AND Akemi Matsuno-Yagi AND Melissa Ritland AND Byoung B. Seo AND Sarah E. LeBoeuf AND Laurie J. Gay AND Takao Yagi AND Brunhilde Felding-Habermann
https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI64264
Rapamycin Plus Doxycycline Combination Affects Growth Arrest and Selective Autophagy-Dependent Cell Death in Breast Cancer Cells. Dankó T, Petővári G, Sztankovics D, Moldvai D, Raffay R, Lőrincz P, Visnovitz T, Zsiros V, Barna G, Márk Á, Krencz I, Sebestyén A.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 27;22(15):8019. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158019. PMID: 34360785; PMCID: PMC8347279.
In Vivo Xenograft Model.
Rapamune (Pfizer – Budapest, Hungary; active ingredient: rapamycin) by gavage at 3 mg/kg body weight; (3) doxycycline (Merck-Sigma-Aldrich)—5 mg/kg body weight.
The treatments were administered three times per week for 3 weeks.
The rapamycin + doxycycline combination was more effective than traditional chemotherapy—doxorubicin in ZR75.1 Breast Cancer Cells.
R + D exhibit synergistic growth inhibitory effects in ZR75.1 and additive inhibition in MDA-MB-231 cells.
Study on the effect of ursolic acid on MMPs and antimetastatic activity in TNBC cells
Artemisinin induces selective and potent anticancer effects in drug resistant breast cancer cells by inducing cellular apoptosis and autophagy and G2/M cell cycle arrest
EGCG Inhibits Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Differentiation into Adipocytes and Prevents a STAT3-Mediated Paracrine Oncogenic Control of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Invasive Phenotype
MYCL promotes the progression of triple‑negative breast cancer by activating the JAK/STAT3 pathway
- pharmacological inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway markedly decreased Myc level and exhibited remarkable therapeutic efficacy in Myc-driven cancers
- insulin upregulates the expression of c-Myc
Reverse engineering of triple-negative breast cancer cells for targeted treatment
Taurine induces the apoptosis of breast cancer cells by regulating apoptosis-related proteins of mitochondria
Low dose of kaempferol suppresses the migration and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells by downregulating the activities of RhoA and Rac1
Kaempferol as a Potential PAK4 Inhibitor in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Extra Precision Glide Docking and Free Energy Calculation
Drug-repositioning screening identified piperlongumine as a direct STAT3 inhibitor with potent activity against breast cancer
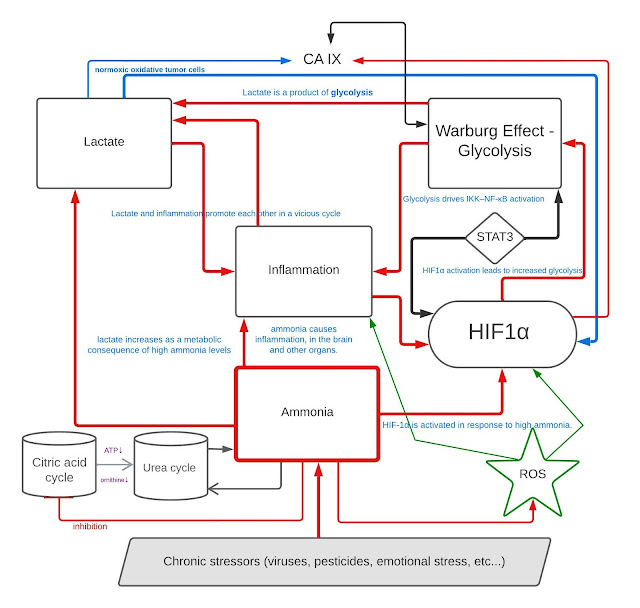
Targeting hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha: A new strategy for triple-negative breast cancer therapy
Lactobacilli Modulate Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF)-1 Regulatory Pathway in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cell Line
Natural Compounds Regulate Glycolysis in Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironment
Identification of Natural Compounds as Inhibitors of Pyruvate Kinase M2 for Cancer Treatment
 |
| click to enlarge image |
Mitochondrial Protein UCP1 Inhibits the Malignant Behaviors of Triple-negative Breast Cancer through Activation of Mitophagy and Pyroptosis
Browning Effects of a Chronic Pterostilbene Supplementation in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet
Naringenin Promotes Thermogenic Gene Expression in Human White Adipose Tissue
Exploring the molecular targets and mechanisms of [10]-Gingerol for treating triple-negative breast cancer using bioinformatics approaches, molecular docking, and in vivo experiments
https://cdn.amegroups.cn/journals/pbpc/files/journals/3/articles/58709/public/58709-PB12-7254-R3.pdf
Diallyl trisulfides, a natural histone deacetylase inhibitor, attenuate HIF-1α synthesis, and decreases breast cancer metastasis
Nicotinamide (niacin) supplement increases lipid metabolism and ROS‐induced energy disruption in triple‐negative breast cancer: potential for drug repositioning as an anti‐tumor agent
Compounds from Natural Sources as Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Gingers and Their Purified Components as Cancer Chemopreventative Agents
The “Yin and Yang” of Natural Compounds in Anticancer Therapy of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers
Apigenin Induces Apoptosis and Blocks Growth of Medroxyprogesterone Acetate-Dependent BT-474 Xenograft Tumors
Apigenin suppresses the stem cell-like properties of triple-negative breast cancer cells by inhibiting YAP/TAZ activity
Matrine suppresses breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion via VEGF-Akt-NF-??B signaling
Carbonic Anhydrase Expression in TNBC Breast Cancer Cells and Human Tumor Grafts
Ornithine and breast cancer: a matched case–control study
Identification for antitumor effects of tramadol in a xenograft mouse model using orthotopic breast cancer cells
The therapeutic potential of targeting tryptophan catabolism in cancer
Naringin is a promising natural compound for therapy of iron-overload disorders "We found that naringin is able to decrease serum iron level in an effective manner, even more potent than the gold standard, desferal."
ROR activation by Nobiletin enhances antitumor efficacy via suppression of IκB/NF-κB signaling in triple-negative breast cancer
Aurora Kinase A and Bcl-xL Inhibition Suppresses Metastasis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36077449/
Drivers and suppressors of triple-negative breast cancer
GPER1 promotes estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cell migration and invasion via non-genomic activation of c-Src/NF-κB/focal adhesion kinase cascade
Chrysin inhibits metastatic potential of human triple-negative breast cancer cells by modulating matrix metalloproteinase-10, epithelial to mesenchymal transition, and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
Anti-cancer Effect of Apigenin on Human Breast Carcinoma MDA-MB-231 through Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
MAPK4 promotes triple negative breast cancer growth and reduces tumor sensitivity to PI3K blockade
Mebendazole prevents distant organ metastases in part by decreasing ITGβ4 expression and cancer stemness
Mebendazole Potentiates Radiation Therapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Honokiol mediated inhibition of PI3K/mTOR pathway: A potential strategy to overcome immunoresistance in glioma, breast and prostate carcinoma without impacting T cell function
β-Catenin Is Required for the Tumorigenic Behavior of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells
miRNA-21 promotes proliferation and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells through targeting PTEN
An FDA-Approved Antifungal, Ketoconazole, and Its Novel Derivative Suppress tGLI1-Mediated Breast Cancer Brain Metastasis by Inhibiting the DNA-Binding Activity of Brain Metastasis-Promoting Transcription Factor tGLI1
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9454738/
HTR1A Inhibits the Progression of Triple‐Negative Breast Cancer via TGF‐β Canonical and Noncanonical Pathways
"The combined treatment of HTR1A agonists with demethylation drugs may significantly improve patient survival."
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9036047/
- Modulation of the tumor microenvironment and inhibition of EGF/EGFR pathway: Novel anti-tumor mechanisms of Cannabidiol in breast cancer {ref}
Polyphenol-Rich Muscadine Grape Extract Reduces Triple Negative Breast Cancer Metastasis in Mice with Changes in the Gut Microbiome
Blueberry Phytochemicals Inhibit Growth and Metastatic Potential of MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells Through Modulation of the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Pathway"The dose of blueberry in our in vivo study is equal to a fresh blueberry intake of 25 grams/kg. With a conversion to human dose (based on surface area) (49), this is equal to 2.03 g/kg human or 122 grams (4.3 oz) of fresh blueberries/day for a 60 kg person. A single serving of fresh blueberries is 6 oz. which is an attainable intake for the average person. Therefore, blueberry intake could be an important part of dietary cancer prevention strategies."
Identification of FOXM1 as a specific marker for triple‑negative breast cancer
The exploration of contrasting pathways in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC)
Bioinformatics driven discovery of small molecule compounds that modulate the FOXM1 and PPARA pathway activities in breast cancer
Exposure of breast cancer cells to hypoxia induces FAK phosphorylation/activation {ref}
Down-regulation of FOXM1 inhibits Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) activity in breast cancer cells {ref}
The Role of PPARs in Breast Cancer
Down-regulation of c-MYC and hTERT gene expression in triple negative breast cancer
Therapeutic Role of Tamoxifen for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Leveraging the Interaction Between ERβ and Mutant p53
Tamoxifen reverses epithelial–mesenchymal transition by demethylating miR-200c in triple-negative breast cancer cells
Modulatory effect of sodium butyrate on anticancer activity of abemaciclib in MDA-MB- 231 human breast cancer cells
Divergent effects of vitamins K1 and K2 on triple negative breast cancer cells
ZHX2 promotes HIF1α oncogenic signaling in triple-negative breast cancer
Targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) signaling with natural products toward cancer chemotherapy
Emodin inhibits epithelial‑mesenchymal transition and metastasis of triple negative breast cancer via antagonism of CC‑chemokine ligand 5 secreted from adipocytes
The Effect of Different Probiotic Bacterial Strains on Ammonia (NH3) Production Levels
(Lactobacillus bulgaricus, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium longum, Saccharomyces boulardii)
Shikonin inhibits triple-negative breast cancer-cell metastasis by reversing the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via glycogen synthase kinase 3β-regulated suppression of β-catenin signaling
Targeting Tumor Acidosis and Regulatory T Cells Unmasks Anti-Metastatic Potential of Local Tumor Ablation in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Curcumin-induced antitumor effects on triple-negative breast cancer patient-derived xenograft tumor mice through inhibiting salt-induced kinase-3 protein
Betulinic acid impairs metastasis and reduces immunosuppressive cells in breast cancer models
Tim-3 promotes cell aggressiveness and paclitaxel resistance through the NF-κB /STAT3 signaling pathway in breast cancer
Rosemary Extract Inhibits Proliferation, Survival, Akt, and mTOR Signaling in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells
Boswellia frereana suppresses HGF-mediated breast cancer cell invasion and migration through inhibition of c-Met signaling
Nerve-driven metastasis
Anticancer effects of sanguinarine in triple-negative breast cancer cells via apoptosis induction and cell cycle arrest
Metastasis of Breast Tumor Cells to Brain Is Suppressed by Phenethyl Isothiocyanate in a Novel In Vivo Metastasis Model
Methylene blue photodynamic therapy induces selective and massive cell death in human breast cancer cells
Baicalein induces tumor suppression in triple-negative breast cancer by mTOR inhibition mediated through DDIT4 expression
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1072751512008046
Effect of telmisartan on triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and lung cancer tumor progression and intratumoral distribution of nanoparticles
Sulforaphane suppresses metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells by targeting the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway
Andrographolide suppresses the malignancy of triple-negative breast cancer by reducing THOC1-promoted cancer stem cell characteristics
Triptonide (Tripterygium wilfordii) effectively inhibits triple-negative breast cancer metastasis through concurrent degradation of Twist1 and Notch1 oncoproteins
The apple polyphenol phloretin inhibits breast cancer cell migration and proliferation via inhibition of signals by type 2 glucose transporter
Quercetin blocks the aggressive phenotype of triple-negative breast cancer by inhibiting IGF1/ IGF1R-mediated EMT program
Simvastatin induced ferroptosis for triple-negative breast cancer therapy
Luteolin inhibits triple-negative breast cancer by inducing apoptosis and autophagy through SGK1-FOXO3a-BNIP3 signaling
Luteolin suppresses the metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer by reversing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via downregulation of β-catenin expression
Identification of novel inhibitors from Urtica spp against MDAMB-231 targeting JAK 2 receptor for breast cancer therapy
Thymoquinone Inhibition of Chemokines in TNF-α-Induced Inflammatory and Metastatic Effects in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells
Phytocannabinoids in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Treatment: Current Knowledge and Future Insights
Rutaecarpine induces the differentiation of triple-negative breast cancer cells through inhibiting fumarate hydratase
Neutrophils in triple-negative breast cancer: an underestimated player with increasingly recognized importance
Capsaicin Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Breast Cancer by Down-Regulating FBI-1-Mediated NF-κB Pathway
Anti-cancer effect of Petasites hybridus L. (Butterbur) root extract on breast cancer cell lines
Myricetin-induced apoptosis of triple-negative breast cancer cells is mediated by the iron-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species from hydrogen peroxide
Nanoemulsion Myricetin preparation increases the anticancer efficacy against Triple-negative Breast Cancer cells {ref}
Tumor-B-cell interactions promote isotype switching to an immunosuppressive IgG4 antibody response through upregulation of IL-10 in triple negative breast cancers
https://translational-medicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12967-022-03319-5
Hibiscus flower extract selectively induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells and positively interacts with common chemotherapeutics
https://bmccomplementmedtherapies.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12906-019-2505-9
Z-Guggulsterone Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by Targeting the p53/CCNB1/PLK1 Pathway in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsomega.2c07480
Phellinus linteus suppresses growth, angiogenesis and invasive behaviour of breast cancer cells through the inhibition of AKT signalling
https://www.nature.com/articles/6604319
Salidroside inhibits migration, invasion and angiogenesis of MDA‑MB 231 TNBC cells by regulating EGFR/Jak2/STAT3 signaling via MMP2
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29901185/
Lovastatin Inhibits EMT and Metastasis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Stem Cells Through Dysregulation of Cytoskeleton-Associated Proteins
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8212055/
Gallic acid suppresses the progression of triple-negative breast cancer HCC1806 cells via modulating PI3K/AKT/EGFR and MAPK signaling pathways
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9744937/
Gallic acid and curcumin induce cytotoxicity and apoptosis in human breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30211078/
Synergies
Wu, Hua-Tao & Li, Chun-Lan & Fang, Ze-Xuan & Chen, Wen-Jia & Lin, Wen-Ting & Liu, Jing. (2022). Induced Cell Cycle Arrest in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Combined Treatment of Itraconazole and Rapamycin. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 13. 873131. 10.3389/fphar.2022.873131
Synergistic anticancer effects of PEITC and Withaferin A on MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells.
In vitro anticancer efficacy of a polyphenolic combination of Quercetin, Curcumin, and Berberine in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells
Akanksha Kashyap a, Sheikh Mohammad Umar, Arundhathi Dev J․R․, Mohini Mendiratta, Chandra Prakash Prasad
Synergistic anticancer action of quercetin and curcumin against triple-negative breast cancer cell lines
Vitamin B2 Sensitizes Cancer Cells to Vitamin-C-Induced Cell Death via Modulation of Akt and Bad Phosphorylation
Enhanced Anticancer Effect of Adding Magnesium to Vitamin C Therapy: Inhibition of Hormetic Response by SVCT-2 Activation
.jpeg) |
| Click to enlarge the diagram |
Beta 2 Adrenergic Receptor Antagonist Propranolol and Opioidergic Receptor Antagonist Naltrexone Produce Synergistic Effects on Breast Cancer Growth Prevention by Acting on Cancer Cells and Immune Environment in a Preclinical Model of Breast Cancer
Zoledronate and Molecular Iodine Cause Synergistic Cell Death in Triple Negative Breast Cancer through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
Synergistic inhibition of the growth of MDA‑MB‑231 cells in triple‑negative breast cancer by salinomycin combined with 17‑AAG (Tanespimycin) and its mechanism
Combined xanthorrhizol-curcumin exhibits synergistic growth inhibitory activity via apoptosis induction in human breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231
Computational pharmacogenomic screen identifies drugs that potentiate the anti-breast cancer activity of statins
A combination of Calcitriol (the activated form of vitamin D3) and ketoconazole exhibit strong inhibitory effects
 |
| click to enlarge the diagram |
Synergy of theophylline reduces necrotic effect of berberine, induces cell cycle arrest and PARP, HMGB1, Bcl-2 family mediated apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells
Combination treatment of bicalutamide and curcumin has a strong therapeutic effect on androgen receptor-positive triple-negative breast cancers
Aspirin in combination with Letrozole or Olaparib induced apoptosis in estrogen receptor-positive T-47D & triple negative MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines
Combinatorial therapy of Thymoquinone and Emodin synergistically enhances apoptosis, attenuates cell migration and reduces stemness efficiently in breast cancer
Synergy between sublethal doses of shikonin and metformin fully inhibits breast cancer cell migration and reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Synergistic apoptotic effect of celecoxib and luteolin on breast cancer cells
Anthocyanin and Gingerol Extracts Exhibit a Synergistic Effect to Inhibit the Proliferation of Caco-2, Hep G2, and HT-29 Cells in Vitro
"Strong synergism levels at high growth inhibitory effects suggest that the anthocyanin–gingerol combination has high potency for the inhibition of cancer cell growth."
[10]-gingerol induces apoptosis and inhibits metastatic dissemination of triple-negative breast cancer in vivo
[10]-Gingerol Affects Multiple Metastatic Processes and Induces Apoptosis in MDAMB- 231 Breast Tumor Cells
Phytochemicals potently inhibit migration of metastatic breast cancer cells
[6]-Gingerol inhibits metastasis of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells
10-Gingerol inhibits proliferation and invasion of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through suppression of Akt and [p38.sup.MAPK] activity
Synergistic Tumoricidal Effects of Alpha-Lipoic Acid and Radiotherapy on Human Breast Cancer Cells via HMGB1 / Journal of the Korean Cancer Association, 대한암학회지
Targeting carbonic anhydrase IX improves the anti-cancer efficacy of mTOR inhibitors
Metformin and propranolol combination prevents cancer progression and metastasis in different breast cancer models
Study of quercetin and fisetin synergistic effect on breast cancer and potentially involved signaling pathways
Doxorubicin + Caffeine + Ivermectin may be an effective anticancer combination
Novel Medicinal Mushroom Blend as a Promising Supplement in Integrative Oncology: A Multi-Tiered Study using 4T1 Triple-Negative Mouse Breast Cancer Model
TNBC recurrence
"8 out of 13 initially triple-negative patients (61.5%) had a change to positive status of either ER, PR, or HER2".{
ref}
HER2+
.jpeg) |
| click to enlarge the diagram |
AKT and MTOR inhibitors are highly synergistic in Her2 breast cancer cell lines. {ref} Thymoquinone can serve as an AKT suppressor.
The Akt pathway in oncology therapy and beyond (Review)
Sirolimus and trastuzumab combination therapy for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer after progression on prior trastuzumab therapy
The mTOR Inhibitor Rapamycin Synergizes with a Fatty Acid Synthase Inhibitor to Induce Cytotoxicity in ER/HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Cells
Successful Treatment of HER2-neu–positive Breast Cancer With Paclitaxel and Trastuzumab Supplemented With Turkey Tail Mushrooms and Community Support
Trastuzumab enhances the anti-tumor effects of the histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium butyrate on a HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cell line
A combination of anti-HER2 and anti-PD-L1 therapy may have synergistic effects. {ref}
HER2 regulates HIF-2α and drives an increased hypoxic response in breast cancer
- Apigenin inhibits Hif1 and Hif2-alpha {ref}
Anthelminthic niclosamide inhibits tumor growth and invasion in cisplatin‑resistant human epidermal growth factor receptor 2‑positive breast cancer
Aspirin and atenolol enhance metformin activity against breast cancer by targeting both neoplastic and microenvironment cells
CCL2/CCR2 Regulates the Tumor Microenvironment in HER-2/neu-Driven Mammary Carcinomas in Mice
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0165595
- Sanguinarine Inhibition of TNF-α-Induced CCL2, IKBKE/NF-κB/ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway, and Cell Migration in Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells {study}
Targeting of PYK2 Synergizes with EGFR Antagonists in Basal-like TNBC and Circumvents HER3-Associated Resistance via the NEDD4–NDRG1 Axis
Dorsomorphin (Compound C) enhances the anticancer effect of aspirin in HER-2-positive breast cancer by regulating lipid metabolism in an AMPK-independent pathway
Apigenin Induces Apoptosis and Blocks Growth of Medroxyprogesterone Acetate-Dependent BT-474 Xenograft Tumors
"Our data clearly show that apigenin (50 mg/kg) inhibits progression and development of these xenograft tumors by inducing apoptosis, inhibiting cell proliferation, and reducing expression of Her2/neu. Moreover, apigenin reduced levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) without altering blood vessel density"
Dose conversion: approx 300mg Apigenin in 75kg human. In the metformin study 240mg.
HER2+ breast cancer cells undergo apoptosis upon exposure to tannic acid released from remodeled cross-linked collagen type I
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28877394/
CYP hydroxylase and sEH metabolites are most significantly elevated in ER−/PR−/HER2+ tumors {ref}
A synergistic antiproliferation effect of curcumin and docosahexaenoic acid in SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells: unique signaling not explained by the effects of either compound alone
"The effect was synergistic for SK-BR-3 (ER- PR- Her2+) relative to the two compounds individually"
MMP-9 expression varies according to molecular subtypes of breast cancer
MMP-9 overexpression revealed itself as a startling feature of triple-negative and HER2-positive breast cancers
Antitumor activity of phenethyl isothiocyanate in HER2-positive breast cancer models.
Antitumor efficacy of Piperine in the treatment of human HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells
Real-time cell analysis of the inhibitory effect of vitamin K2 on adhesion and proliferation of breast cancer cells.
Natural Compound Attacks HER2 Positive Breast Cancer Cells
Selective Anti-Proliferation of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Cells by Anthocyanins Identified by High-Throughput Screening
"Two of the hit compounds, peonidin-3-glucoside and cyaniding-3-glucoside, are both extracts from black rice. "
Oleic acid, the main monounsaturated fatty acid of olive oil, suppresses Her-2/neu (erbB-2) expression and synergistically enhances the growth inhibitory effects of trastuzumab (Herceptin) in breast cancer cells with Her-2/neu oncogene amplification
The Potential Utility of Curcumin in the Treatment of HER-2-Overexpressed Breast Cancer: An In Vitro and In Vivo Comparison Study with Herceptin
Growth Suppression of HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer Cells by Berberine via Modulation of the HER2/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
Melatonin Represses Metastasis in Her2-Positive Human Breast Cancer Cells by Suppressing RSK2 Expression
Synergistic Anti-Cancer Potential of Phenethyl Isothiocyanate and Curcumin Induces Apoptosis and G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Cells
HER2 and ER signaling cross-talk
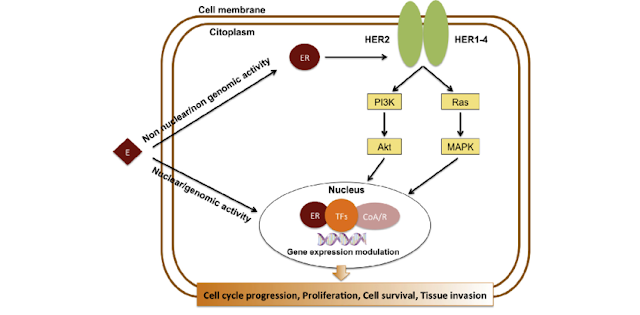 |
Estrogens (E) act via a non nuclear/non genomic activity and a nuclear/genomic activity. Non nuclear estrogen receptor (ER) interacts directly or indirectly (e.g. via G proteins) with human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER)2/HER1-4 dimers activating their downstream kinase pathways (e.g. Ras-MAPK and PI3K-Akt pathways), which in turn phosphorylate ER and other transcription factors (TFs) and coactivators/corepressors (CoA/R), modulating gene expression. HER2 signaling pathways also reduce ER expression at both mRNA and protein levels. ER also promotes HER2, other tyrosine chinese receptors (TKR) and TKR ligands' gene expression. This bidirectional cross-talk leads to cancer cell cycle progression, proliferation, survival and invasiveness. {ref}
Characterization of synergistic anti-cancer effects of docosahexaenoic acid and curcumin on DMBA-induced mammary tumorigenesis in mice
|
ER+/PR+
Interactions Between Natural Products and Tamoxifen in Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Literature Review
⚠ Vitamin C attenuates the cytotoxicity of tamoxifen. Vitamin C suppresses cell death in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells induced by tamoxifen.
⚠ Iodine stimulates estrogen receptor singling and its systemic level is increased in surgical patients due to topical absorption
 |
| Iodine vs Potassium Iodide (KI). KI doesn't doesn´t stimulate ER in TNBC but there is some stimulation in estrogen-positive cell line. Iodine stimulates ER in both cell lines. |
Combined Luteolin and Indole-3-Carbinol Synergistically Constrains ERα-Positive Breast Cancer by Dual Inhibiting Estrogen Receptor Alpha and Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Pathway in Cultured Cells and Xenograft Mice
Green tea increases the effectiveness of tamoxifen
Grape Seed Procyanidins Inhibit the Growth of Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells by Down-Regulating the EGFR/VEGF/MMP9 Pathway
Prevention of Bone Loss by Zoledronic Acid in Premenopausal Women Undergoing Adjuvant Chemotherapy Persist up to One Year following Discontinuing Treatment
Modulating the Activity of Androgen Receptor for Treating Breast Cancer
Case Reports
Case report of long-term survival with metastatic triple-negative breast carcinoma
Long-Term Non-progression in Metastatic Breast Cancer Beyond 5 Years: Case Series and Review
Long-Term Progression-Free Survival of Stage IV Triple Negative Breast Cancer Patient having Genetic Mutation with Variant of Uncertain Significance and Lung Metastasis: A Case Report Emphasizing Role of Ayurvedic Treatment
Breast Cancer With Brain Metastases: Perspective From a Long-Term Survivor Christopher P. Kofron, PhD and Angela Chapman, PhD
Significant response of low-dose apatinib monotherapy in brain metastases of triple-negative breast cancer: A case report
Laika tnbc protocol {ref}
Dose calculations
Metformin 760mg
+ Apigenin 243mg
{ref} Ketoconazole 200 mg tablets, 2 tablets orally TID
+ Calcitriol (0.5 mcg caplets) given in escalating doses, orally QD X3 consecutive days every week
{ref} Rapamycin 18mg
+ Doxycycline 30mg (3x/week for 21 days)
{ref} Doxycycline approx 350mg
{ref} Honokiol + Fluvastatin 20-80mg/d {ref}
Emodin (30- 60mg) {ref}
Magnolol (120 - 600mg)
{ref | ref} Quercetin approx 1300mg
{ref} Magnesium sulfate (approx 600mg) {ref}
Betulinic acid (approx 50mg) {ref}
Hesperidin (approx 600mg) {ref}
To calculate the dose for a different weight e.g. 55kg
75kg → estimated dose e.g 760mg
Diet
Artificial diets with selective restriction of amino acids and very low levels of lipids induce anticancer activity in mice with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer
Divergent effects of vitamins K1 and K2 on triple negative breast cancer cells
"To assess differential effects of vitamin K, TNBC cells were cultured in media supplemented with K1 or K2.
K1 treatment increased cell growth, and enhanced stemness and GLA-modified protein expression in TNBC lysates. Alternatively, lysates from cells exposed to vehicle, K2, or the VKOR antagonist, warfarin, did not express GLA-modified proteins. Further, K2 exposure reduced stemness and elicited anti-proliferative effects. "
Vitamin K1 is said to have a lower absorption rate than vitamin K2, with estimates as low as 10% of the vitamin being absorbed. This could be because K2 foods are often richer in fat, whereas K1 sources are often leafy green vegetables which are low in fat. Hence, eating foods with high amounts of K1 such as kale together with fats like olive oil, coconut oil or avocado could boost absorption significantly.
Fruits don't contain a high amount of K1.
Vegetables High in K1
Kale (cooked) — 443% of the DV per serving
Mustard greens (cooked) — 346% of the DV per serving
Swiss chard (raw) — 332% of the DV per serving
Collard greens (cooked) — 322% of the DV per serving
Spinach (raw) — 121% of the DV per serving
Broccoli (cooked) — 92% of the DV per serving
Vegetables Low in Vitamin K1 , per 1-cup serving, include:
Turnips (raw or cooked) — 0.1 micrograms
Beets (raw or cooked) — 0.3 micrograms
Sweet Corn (raw or cooked) — 0.5 micrograms
Onion (raw or cooked) — 1 microgram per 1 medium onion
Rutabagas (raw or cooked) — 0.5 micrograms
Pumpkin (cooked) — 2 micrograms
Winter squash(cooked) — 2 micrograms
Summer squash (cooked) — 3 micrograms
Eggplants (cooked) — 3 micrograms
Bamboo shoots (raw or canned) — 0 micrograms
Mushrooms (raw or cooked) — 0 micrograms
Tomatoes (cooked) — 7 micrograms
Tomatoes (raw) — 14 micrograms
Carrots — 16.9 mcg
Cucumbers (raw) — 17 micrograms
Iceberg lettuce (raw) — 17.4 micrograms
Diet may influence the spread of a deadly type of breast cancer, study finds https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2018/02/180207140401.htm "by limiting an amino acid called asparagine in laboratory mice with triple-negative breast cancer, they could dramatically reduce the ability of the cancer to travel to distant sites in the body. Among other techniques, the team used dietary restrictions to limit asparagine."
Norepinephrine induces migration in breast cancer
Effects of neurotransmitters on the chemokinesis and chemotaxis of MDA-MB-468 human breast carcinoma cells. http://europepmc.org/article/MED/12889599
Resting energy expenditure in short-term starvation is increased as a result of an increase in serum norepinephrine https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/71/6/1511/4729485
"an increase in the norepinephrine concentration from 1716. ± 574 pmol/L on day 1 to 3728 ± 1636 pmol/L on day 4 (P < 0.05). Serum glucose decreased from 4.9 ± 0.5 to 3.5 ± 0.5 mmol/L (P < 0.05), whereas insulin did not change significantly."
Norepinephrine concentration more than doubled during short-term starvation.
Dietary Supplementation of Inulin Contributes to the Prevention of Estrogen Receptor-Negative Mammary Cancer by Alteration of Gut Microbial Communities and Epigenetic Regulations https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/24/10/9015
Exercise
Hypothesis
Clinical Trials
Drug Interactions
Always consult a healthcare professional. Check for multi-drug interactions including alcohol, food, and supplements.
Using metformin together with celecoxib or similar anti-inflammatory medications may increase the risk of a rare but serious and potentially life-threatening condition known as lactic acidosis, which is a buildup of lactic acid in the blood that can occasionally occur during treatment with metformin-containing products.
Interactions Between Natural Products and Tamoxifen in Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Literature Review
Dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt can interfere with your body's ability to absorb doxycycline, especially if you consume dairy products around the same time that you take this medication. This is due to the presence of calcium in dairy products.
Current Therapeutic Strategies for Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: From Pharmacists’ Perspective
Phase 1 Study of Erlotinib and Metformin in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Conclusion: Erlotinib and metformin were well tolerated in a population of pretreated mTNBC patients but did not demonstrate efficacy in this population.
Cyproheptadine significantly improves the overall and progression-free survival of sorafenib-treated advanced HCC patients
Functional Profiling
Functional profiling is a laboratory technique that measures how cancer cells respond when exposed to a variety of drugs and drug combinations.
Support groups
Many findings in the above-listed studies are preclinical and have not been validated in human studies.
For informational and research purposes only; none of my writing should be considered medical advice.
Last update: September 24, 2023


.jpeg)



.jpeg)
.jpeg)


.jpeg)



%20(3).png)

No comments:
Post a Comment